Finally, let's quickly go over communication via TCP sockets. This is very similar to the WebSocket implementation, with one key difference: you'll need a separate application on the client side to access the TCP socket.
On Windows, the recommended application is PuTTY, while on Linux and Mac, you can use the built-in telnet terminal application. Instructions on how to install and configure these tools can be found in the installation section.
Connecting with PuTTY (Windows)
To connect to your device using PuTTY, you'll need the device's IP address and the port number. The IP address varies per device, but for TCP connections, the standard port is usually 23.
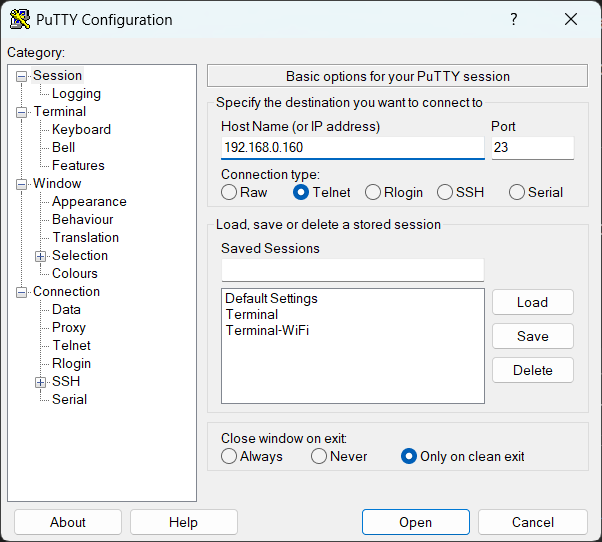
PuTTY Config
Connecting with Telnet (Linux/Unix/Mac)
On Linux, Unix, or macOS, you can use the following command in the terminal:
For example:
One tricky part with telnet is exiting the session. To do so, press CTRL + ], which will bring up the Telnet command prompt. Then type quit and press Enter to close the connection.
Whole Code
#define TCP_PORT 23
char ssid[] = "Replace With Your SSID";
char pass[] = "Replace With Your Password";
uint8_t printBuffer[ 100 ];
int printBufferSize = sizeof( printBuffer );
uint8_t passwordHash[] = { 0xCC, 0xb4, 0x24, 0x83 };
const char logo[] =
" _____ __ ____ _ __ \r\n"
" / ___// /_ ___ / / /___ ___ (_)___ ____ _/ /_____ _____\r\n"
" \\__ \\/ __ \\/ _ \\/ / / __ `__ \\/ / __ \\/ __ `/ __/ __ \\/ ___/\r\n"
" ___/ / / / / __/ / / / / / / / / / / / /_/ / /_/ /_/ / / \r\n"
"/____/_/ /_/\\___/_/_/_/ /_/ /_/_/_/ /_/\\__,_/\\__/\\____/_/ \r\n"
"\r\n\033[0;37m"
"Visit on GitHub:\033[1;32m https://github.com/dani007200964/Shellminator\r\n\r\n"
;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to Network");
while( WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED ){
Serial.print( '.' );
delay( 1000 );
}
Serial.print("Connected!");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
shell.enableBuffering( printBuffer, printBufferSize );
shell.setPassword( passwordHash, sizeof( passwordHash ) );
shell.begin( "arnold" );
tcp.attachConnectCallback( userConnectedCallback );
tcp.attachDisconnectCallback( userDisconnectedCallback );
tcp.attachDebugChannel( &Serial );
tcp.begin();
}
void loop(){
tcp.update();
shell.update();
delay( 2 );
}
shell.printLoginScreen();
}
shell.logOut();
}
